# Process template
Process template are written in NEON (opens new window), take a first look at this format.
This is complete list of all required and optional template configuration options.
Required
Optional
# Process
Process allows define name of process (name) and description (description).
- name (required) - name of process template
- version (required) - for process architects to keep track of template states
- only accepts
<digit>.<digit>.<digit>or<digit>.<digit>.<digit>-<a-zA-Z0-9_>eg. (0.0.1,1.0.2-concept)
- only accepts
- description (optional) - description of process template
process:
name: New connection
version: 1.4.2
description: '''
# New connection
- item 1
- item 2
'''
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# ACL
Process ACL are defined by subsection roles in which are users assigned to individual roles.
Users are selected through their unique identifier (ID) or user group.
acl:
roles:
technician: [ 1,2,3,4,5 ]
accountant: [ 7,8,9 ]
2
3
4
# Magic roles
Magic roles are prefixed with @ and are usually defined by system. We have two magic roles at this moment.
- @creator
Listed users in @creator have the rights to start the process, no-one else. Except the admin from administration.
acl:
roles:
@creator: [ 1,2,3 ]
2
3
- @supervisor
Listed users in @supervisor have the rights to supervise (control) given process. There's a special tab called "Supervisor" on the process detail.
acl:
roles:
@supervisor: [ 1,2,3 ]
2
3
# User groups
User groups are prefixed with % and aggregate users in predefined virtual groups. Useful when you don't want to modify process template all the time.
acl:
roles:
@creator: [ &admins ]
technicians: [ 1,2,&viptechnicians ]
2
3
4
Only users in user group admins can create the process. In resolver role technicians are users (1,2) and all users in user group viptechnicians.
# Steps
Step is basic building stone of processing.
It consist of:
title(optional) - user-friendly title (default value is step id)type(optional) - START / MANUAL (default) / AUTO / ASYNC / END / END_USERexpiration(optional) - expiration of step which defaults to 1 dayacl(optional) - ACL definition for step which defaults toresolver: @creatorresolver(required) - who will resolver the step- You can use in this role:
- Reference role name, e.q.
technicianor@creator.
- Reference role name, e.q.
- You can use in this role:
reader(optional) - who has read access to the step (cannot perform next)- You can use in this role:
- Re-use existing role reference, e.q.
technicianor@creator. - Reference user directly, e.q.
10, 15, 20. - Reference application-based user group, e.q.
&admins,&viptechnicians, etc.
- Re-use existing role reference, e.q.
- You can use in this role:
transitions(optional) - transitions to subsequent steps- at least one must be defined if step is not ending
- only one transition must evaluated truthy at time
layout(optional) - panels layout for specific stepmeta(optional) - step metadata for inbox and calendarevents(optional) - step eventsscripting(optional) - scripting utilityevent(optional) -on_step_start(default) /on_step_end/on_step_completionscript(required) - php script
steps:
sample1:
title: Sample step 1
type: START / MANUAL / AUTO / ASYNC / END / END_USER / SUMMARY
expiration: +1 hour
acl:
resolver: accountant
reader: [ technician, @creator, &admins, 10 ]
transitions:
step1:
expression: "{$customerId === 1000}"
step2:
expression: "{in_array($plan, ['free', 'vip']}"
meta:
inbox:
description: "{$issue->subject}"
calendar:
title: "{$issue->subject}"
description: "{$issue->description}"
location: "{$issue->location}"
layout:
# ↓ see section layout ↓
blueprint:
# ↓ see section blueprint ↓
extra:
# ↓ see section extra ↓
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
Each process template must have one **START** step and at least one **END** or **END_USER** step. **SUMMARY** step is created automatically, but you can override it.
# Types
START - Each process need its first step to by properly started.
MANUAL - Manual (most often) step. It requires user interaction.
AUTO - Step which is done automatically after user interaction. It is not running in background.
This step is resolved automatically, without user interaction. It's resolved in the same request to server as previous step, so don't use it for heavy tasks. We're suggesting to use it for simple automatization.
ASYNC - Step which is done automatically in background. This step need to be triggered, e.g. by cron.
This step is resolved automatically, without user interaction. It's resolved in the background process, so you can use it for heavy (time) tasks. Cron is scheduling every 10 minutes to resolve all waiting async steps.
END - Step is automatically completed if it get into this step. User interaction is not required,
END_USER - Step requires user interaction to be completed.
SUMMARY - Displayed if process is completed.
Summary step is special. It's created by default under the name
summary. You can override it, but name your stepsummary. otherwise it won't work.steps: summary: title: "Order summary" type: SUMMARY expiration: now acl: # Resolver is useless, but required resolver: @creator # Who can display the summary step # Creator and some other users reader: [@creator, 2, 3, 10] layout: # ↓ see section layout ↓1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# Transitions
For evaluation of transition from step to step is used Lattenizer.
You can define more transitions for one step, but only one condition must be true at time. System otherwise do not allow transition to next step.
# Meta
Using meta key you can provide more detailed and user-friendly information in Inbox and in Calendar.
meta:
inbox:
description: "Issue #{$issue}"
calendar:
title: "Issue #{$issue}"
description: "{$issue_message}"
location: "{$issue_address}"
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Extra
Each step has a configuration option extra to store additional informations.
Messages
You can override default messages if system try to move process to next step. For each step differently.
steps:
sample1:
extra:
messages:
next_failure: "Have you fill all forms? Are you sure?"
next_success: "Everything OK, see you buddy!"
2
3
4
5
6
Features
Feature toggles are a powerful technique, allowing modify system behavior.
Current toggles:
ajax- Each panel saves his state by himself without redirecting or refreshing page. Previously called saver. The next panel is a main trigger to perform save operation to all panels, a.k.a one button to save it all.steps: sample1: extra: features: ajax: true1
2
3
4
5
# Variables
Variables are concept which allow you control process and define multiple ways how to complete it.
Actually are variables divided into 2 types:
- json - complex structure (contains multiple specific (scalar) values)
- scalar - specific value (true/false, 1-X,
foo)
Each variable must have:
$key(required) - unique ID of variabletitle(required) - user-friendly variable nametype(required) - type of variable (scalar/json)
Also you could define:
value(optional) - define default value, which is set into variable contain when process startspec(optional) - specification of variable (actually:files,processes)
variables:
# Scalar
customer:
title: Name of customer
type: scalar
value: John Smith
# JSON
customers:
title: Customers
type: json
value: [ 1,2,3 ]
# JSON (file)
file1:
title: First file
type: json
spec: files
# JSON (processes)
processes:
title: Processes
type: json
spec: processes
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# Formation
Key formation defines what kind of rendering is used. Long time we have only layout mode, but at this time we have also blueprint.
formation:
# Rendering blueprint
render: blueprint
# Rendering layout
render: layout
2
3
4
5
6
Pick between blueprint or layout. Blueprint is for advanced users and it's really low level. As the opposite layout is for basic users and has it's own limitation.
# Blueprint
Key blueprint defines blueprint of panels and template for specific step.
Process blueprint
There is no blueprint for whole process. Only for process steps.
Step blueprint
Blueprint is defined on step and has 2 required keys panels and template. Panels names must be unique.
steps:
start:
blueprint:
panels: { ...definition }
script: ""
template: ""
2
3
4
5
6
Learn more about blueprints at Panelus.
# Layout
Key layout defines layout of panels for process or for specific step.
Process layout
layout:
# Extending layout
extends: default
# Sections with panels
sections:
{ ...definition }
2
3
4
5
6
7
Step layout
steps:
sample1:
title: Sample step #1
layout:
# Extending layout
extends: minimal
# Don't extends from any layout,
# don't use it with extends
exclusive: false
# Sections with panels
sections:
{ ...definition }
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
If you want extends other defined layout, use extends key. For example, we have somewhere defined minimal layout and we want to use them in our process.
Learn more about layout at Panelus.
# Extra
# Snippets
Process scoped snippets can be defined in section extra. Snippets can be defined in name => template manner. If both process scoped and general snippets exists with same name, process scoped snippet is used.
extra:
snippets:
snippetName: 'Good day {$name}'
snippet2Name: 'Good evening {$name}'
2
3
4
In lattenizer snippets can be used this way:
{include 'snippetName.snippet', name=>'Adam'}
# Grant access
Users without read permissions to a process can request access. If grant_access is enabled, user accessing a forbidden process will be able to request permission to the process instead of being redirected back to his inbox. Upon requesting access, all users in roles will receive an email with a link that can be used to add requesting user as a reader to all process steps.
extra:
grant_access:
enabled: true
roles: [role1, role2]
2
3
4
# Events
During process are launched predefined events which you can respond to, e.g. with callbacks.
| Scope | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| process | on_process_start | Launched on new process initialization. |
| process | on_process_complete | Launched on process completion. |
| step | on_step_start | Launched on new/next step initialization. |
| step | on_step_end | Launched on step next tryout. |
| step | on_step_completion | Launched on active step completion. |
# Lifecycle
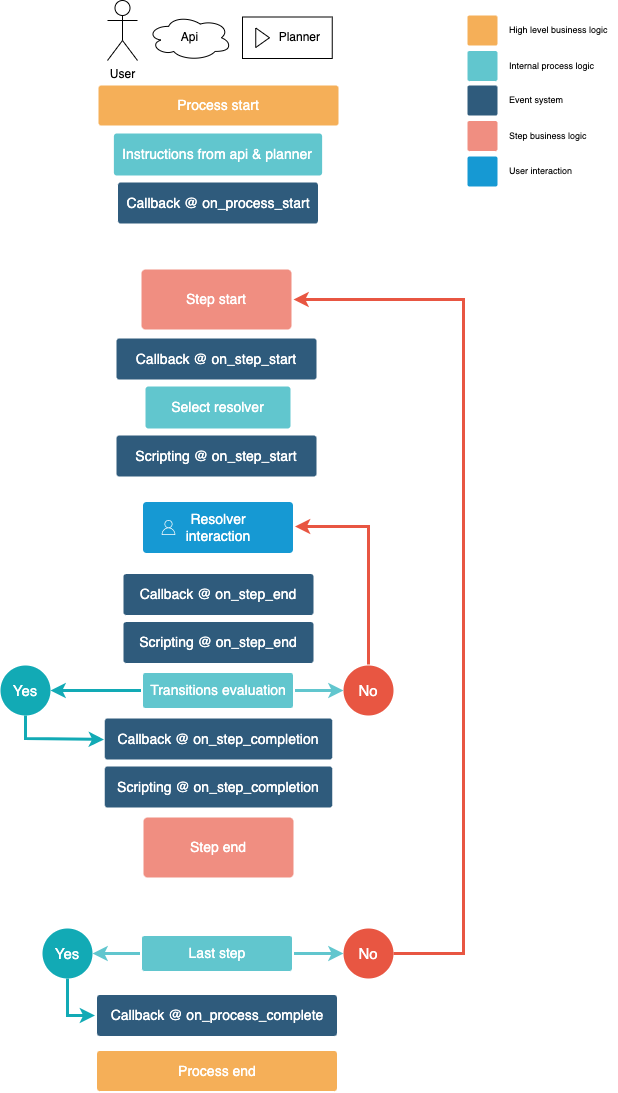
| Action | Call stack | Description |
|---|---|---|
| New process |
1. Internally write log on wall 2. Fill process with variables, roles, tags etc. from api & planner instructions 3. Trigger callback on_process_start on the first step4. Trigger callback & scripting on_step_start on the first step5. Internally compute inbox field for the first step 6. Internally autoselect resolver for the first step | |
| Next step |
1. Trigger callback & scripting on_step_end on the current step 2. Internally lookup and evaluate next step 3. Trigger callback & scripting on_step_completion on the current step4. Internally move to next step 5. Trigger callback & scripting on_step_start on the next step6. Internally compute inbox field for the next step 7. Internally autoselect resolver for the next step | |
| Complete process |
1. Trigger callback & scripting on_step_end on the current step 2. Internally lookup for the summary step 3. Trigger callback & scripting on_step_completion on the current step4. Internally move to summary step 5. Trigger callback on_step_start on the summary step6. Internally compute inbox field for the summary step 7. Internally autoselect resolver for the summary step 8. Internally write log on wall 9. Trigger callback on_process_end |